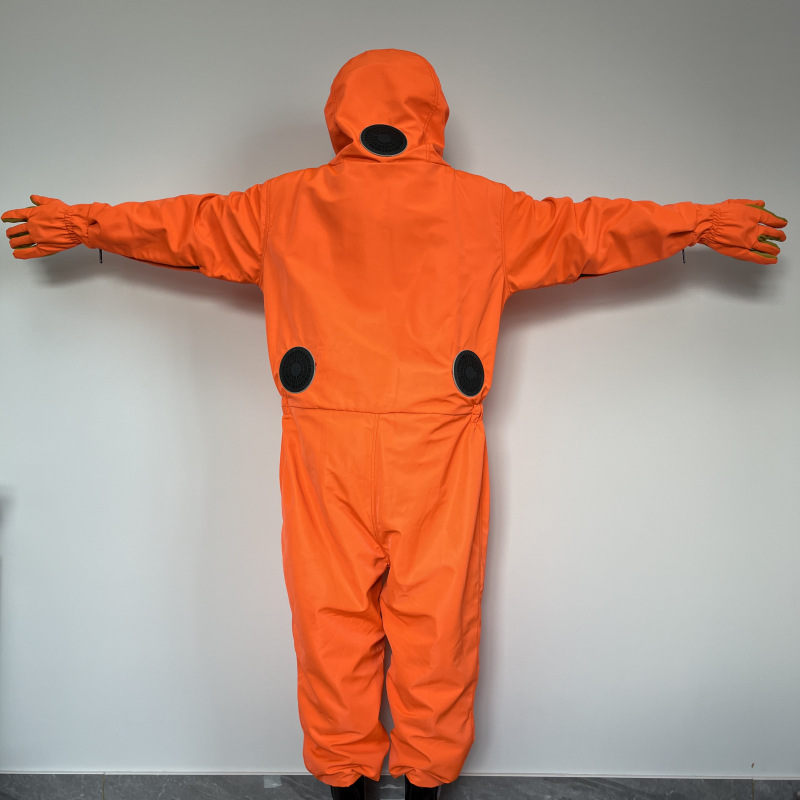
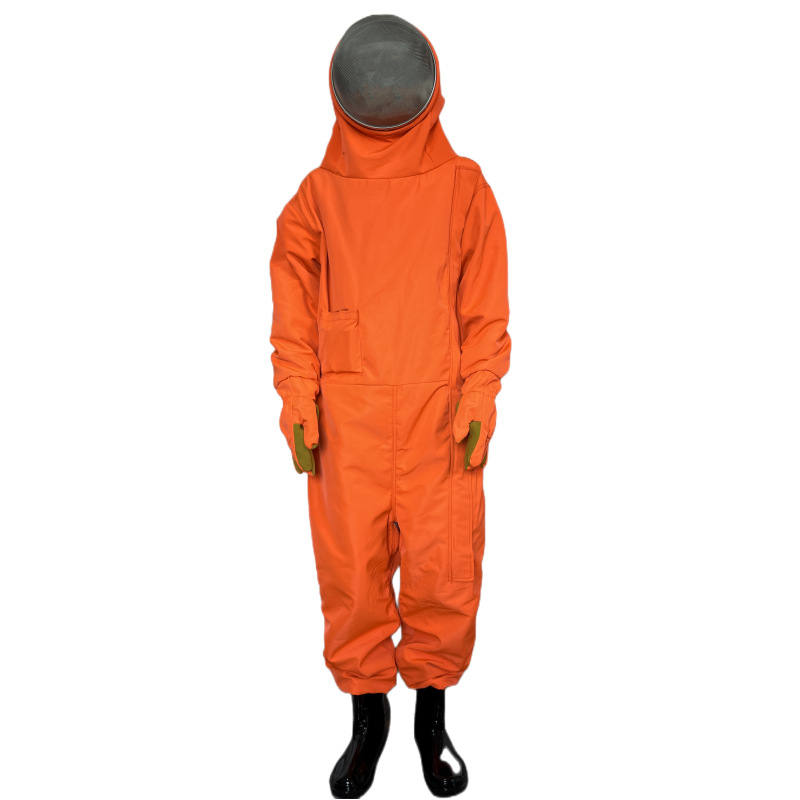
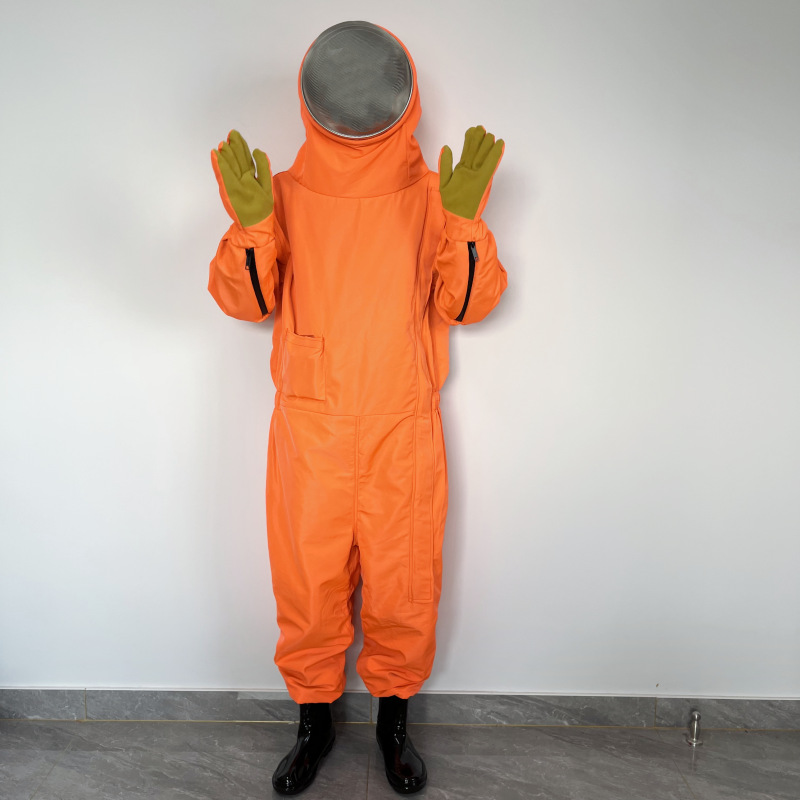
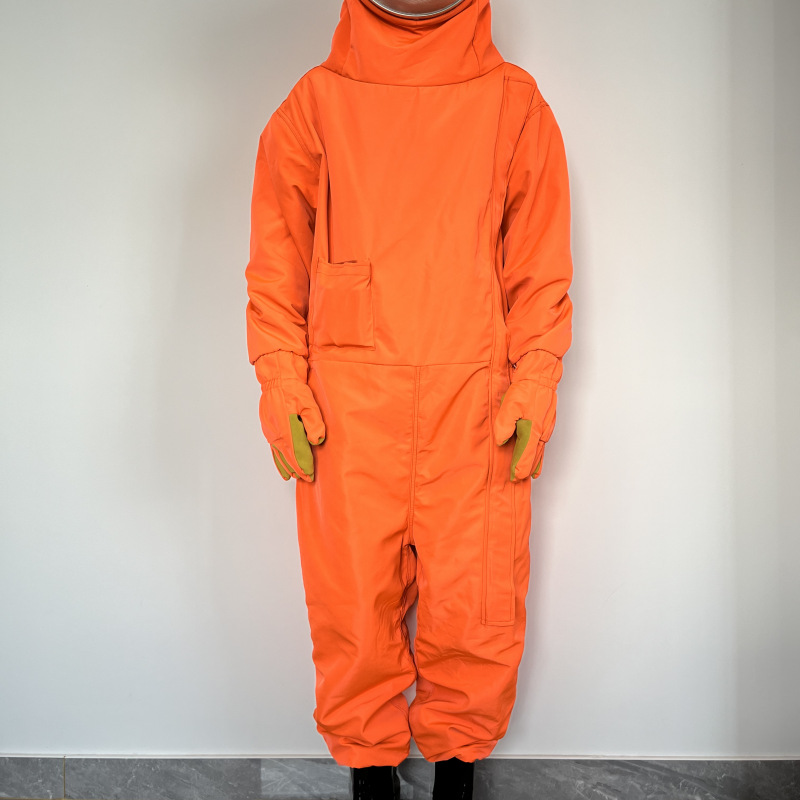
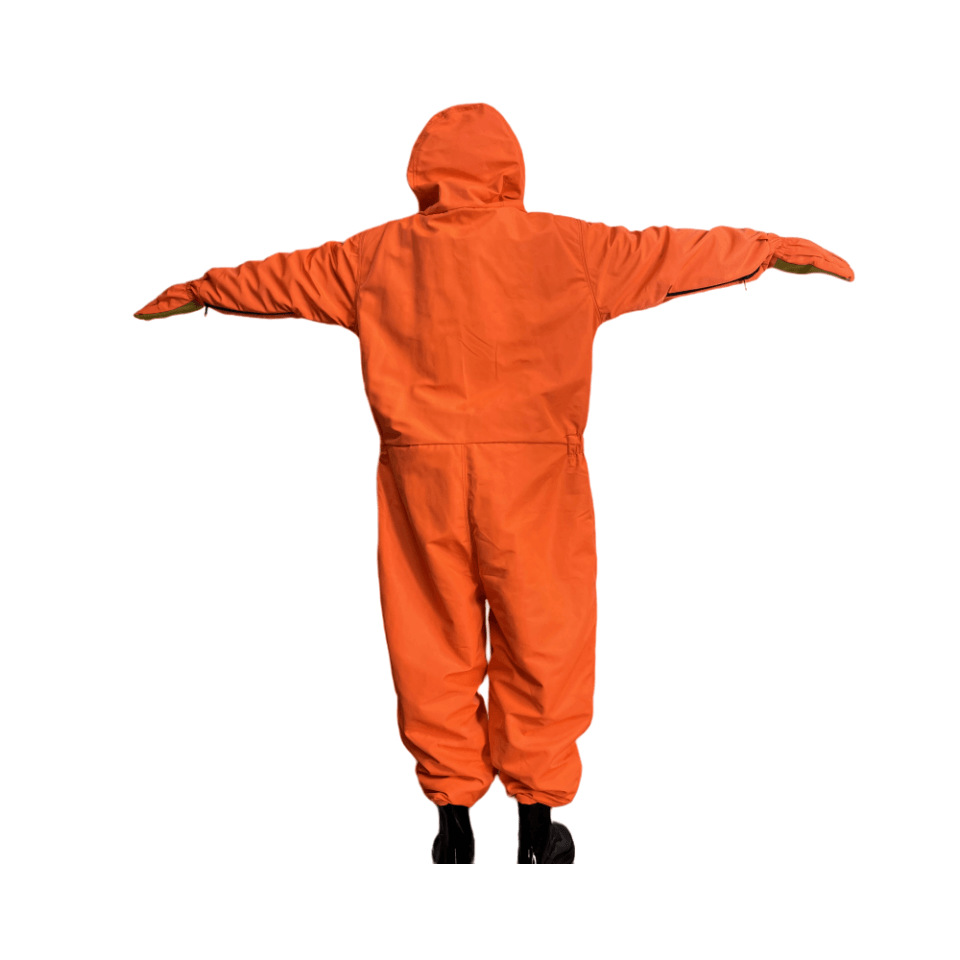
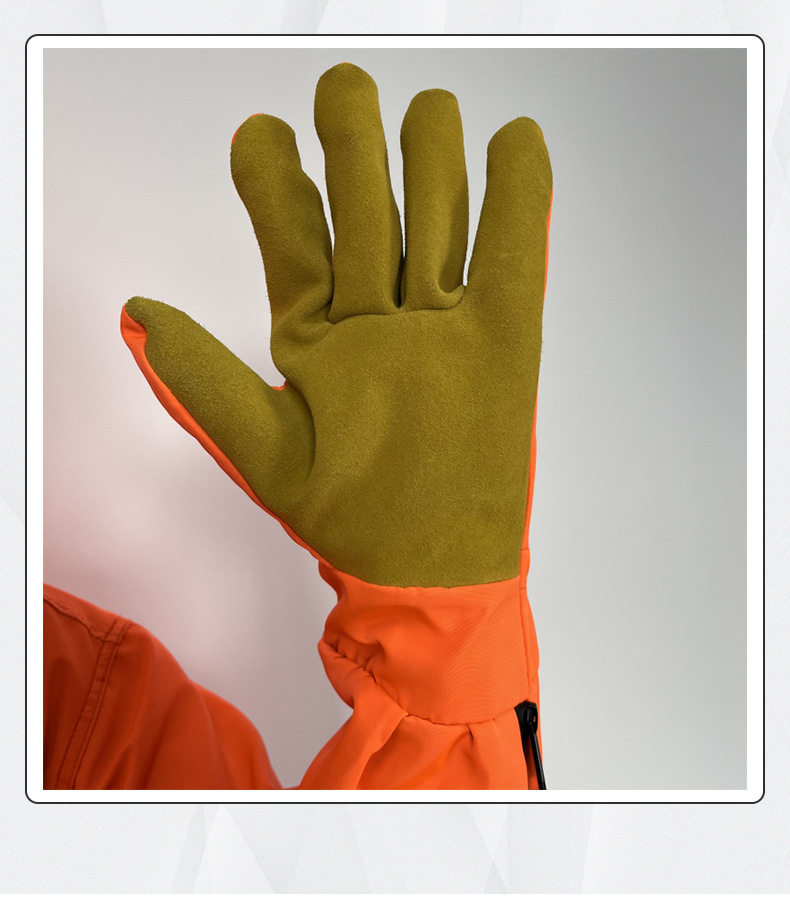
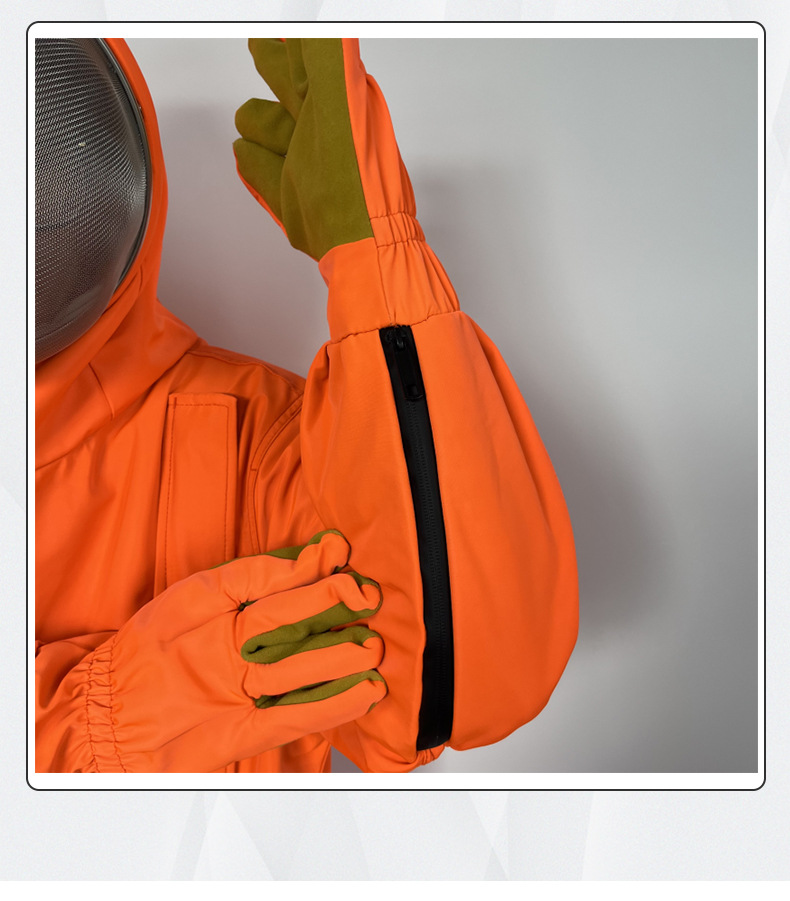
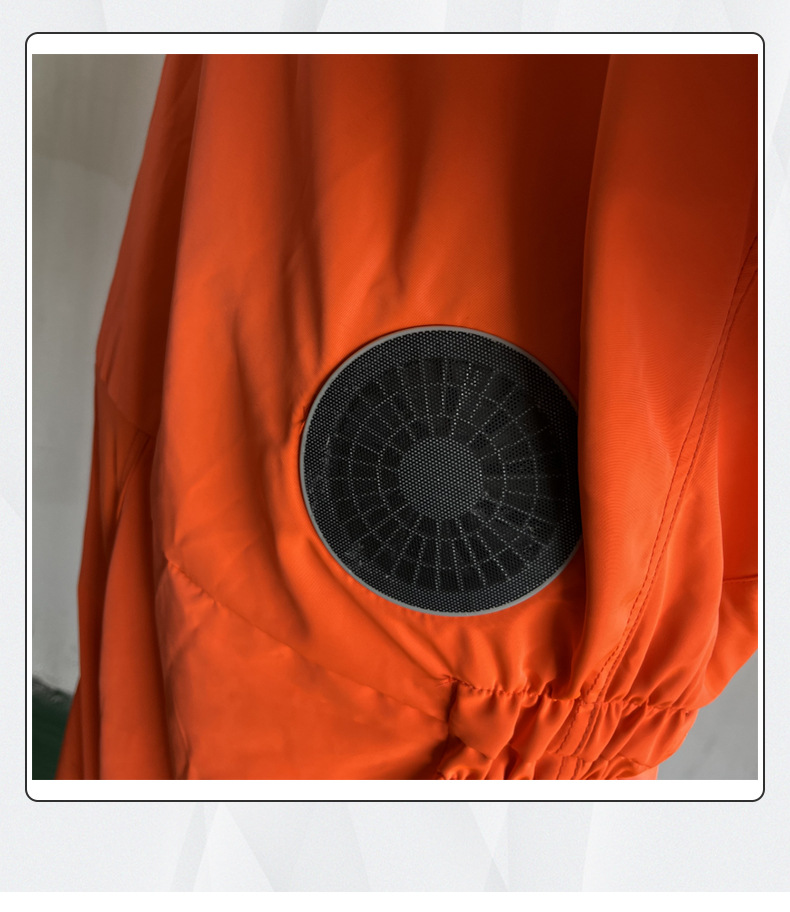
Protective clothing is specialized attire designed to shield individuals from various workplace hazards, ensuring their safety and well-being in challenging environments. These garments are engineered to provide a barrier against a wide range of dangers, including physical, chemical, biological, thermal, and electrical hazards.
The features of protective clothing vary widely based on the specific risks they are designed to address. For instance, in chemical industries, protective clothing often includes chemical-resistant materials to guard against corrosive substances. In healthcare, it includes gowns, gloves, masks, and face shields to prevent the spread of infections.
In construction and industrial settings, protective clothing may comprise hard hats, steel-toed boots, reflective vests, and gloves to mitigate the risks of falling objects, machinery accidents, and exposure to extreme temperatures.
Key attributes of protective clothing include durability, comfort, and compliance with industry-specific safety standards. Ergonomic designs, adjustable straps, and ventilation systems enhance wearer comfort during prolonged use.
Employers play a critical role in providing and enforcing the use of appropriate protective clothing to minimize workplace accidents and health risks. It not only protects workers but also contributes to a culture of safety. Protective clothing is an indispensable component of ensuring occupational safety and preventing injuries or illnesses in diverse workplaces.